The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is made of receptors and signaling molecules that play a pivotal role in the body’s inflammatory response. Activating the ECS with cannabis is an option to help alleviate the discomfort from a chronic illness; an option that many cannabis consumers have found great success in dealing with constant pain
and inflammation from medical ailments.
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to infection and/or physical damage. It signals repair to injured tissue or tags the removal of assaulting pathogens. Inflammation can be good, for example a paper cut will trigger an inflammatory response to swell and knit the wound back together. Chronic inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis, is an example of “bad” inflammation when the natural defense system of the body goes unchecked and triggers swelling and discomfort where there is
no injury or invading pathogen.
There are two major components to the human endocannabinoid system. Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB2). CB1 receptors are heavily expressed in the brain. CB1 interacts with THC to give you the psychoactive “high” felt when smoking cannabis. CB2 receptors are more abundant in the periphery immune system.
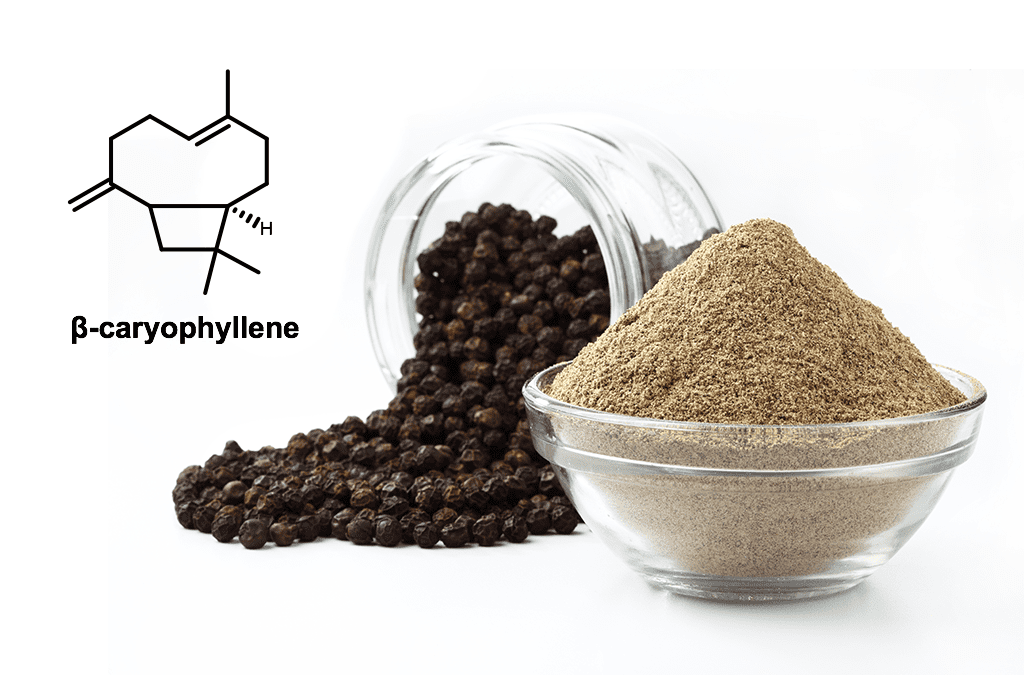
β-caryophyllene is an aromatic terpene found in many cannabis strains, green leafy vegetables, and common kitchen spices. On a chemical level, β-caryophyllene is a large terpene, larger than common terpenes like limonene or myrcene. β-caryophyllene is also a unique terpene because it activates CB2 receptors in the immune system(1). This can be a therapeutic strategy when selecting a cannabis strain for your own personal needs. In 2008, German research showed that β-caryophyllene binds to the
THC binding site of CB2. CB2 receptors have been shown to inhibit inflammation, edema formation, and have pain reducing effects (1). This leads to cellular activation and anti-inflammatory effect. In combination with THC, which primarily binds to CB1 receptors in the brain, β-caryophyllene binding to the periphery CB2 receptors can
provide a stacked pain relieving effect. β-caryophyllene is the only cannabis derived terpene to bind to a CB receptor with a chemical structure that is fundamentally different than traditional cannabis molecules.
If you are turning to cannabis for the therapeutic benefits against inflammation or pain, a high β-caryophyllene strain is a good option. β-caryophyllene will partake a spicy peppery scent similar to cloves or cinnamon. Strains high in β-caryophyllene will be musky and have a funky scent in the back of your sinus, similar to fresh cracked black pepper.
Resources:
1. Gertsch, J., Leonti, M., Raduner, S., Racz, I., Chen, J.-Z., Xie, X.-Q., … Zimmer, A.
(2008). Beta-caryophyllene is a dietary cannabinoid. Proceedings of the National
Academy of Sciences, 105(26), 9099–9104. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0803601105