Cannabis Biology: The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system that’s found throughout the entire body. The human body naturally produces endocannabinoids to help regulate the central nervous system (aka the brain) and the peripheral nervous system (aka the rest of your body). Therefore, we have cannabinoid receptors located throughout our body. In addition, we naturally produce endocannabinoids to regulate memory recall, mood, appetite and pain.
Introducing cannabinoids (aka medical marijuana) creates biological effects in the endocannabinoid system depending on what we ingested and how (aka varieties of highs; body vs. cerebral and everything in between). In effect, CB1 and CB2 are activated and the science begins.
Two receptors have been identified as CB1 and CB2. CB1 is mainly found in the brain. Conversely, CB2 is mainly found in the immune system. However, both are widespread throughout the human body.
CB1 naturally accepts the neurotransmitter anandamide. Anandamide binds to CB1 to regulate memory, sleep, and pain stimuli in the brain. Lastly, anandamide binds to CB2 in the rest of the body to control the immune system.
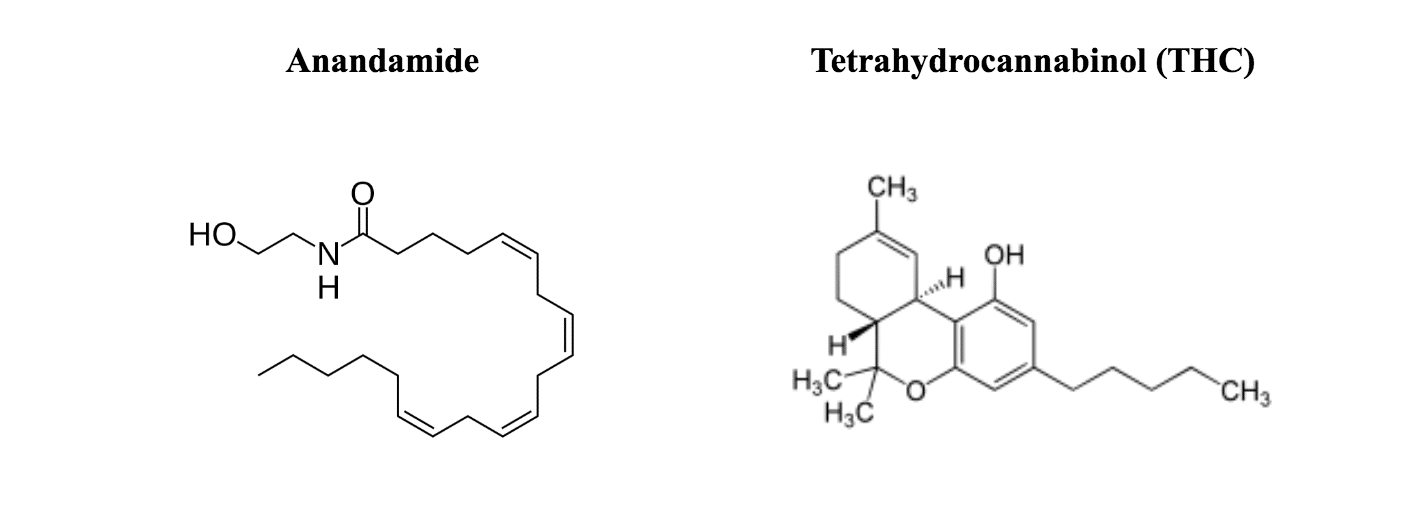
Humans have Marijuana Receptors
That was a heavy intro to the basic science of cannabis, nonetheless, what is the one thing you should take away from this week’s lesson?
- Humans have marijuana receptors in their body.
- When medical marijuana is consumed, endogenous receptors are stimulated.
- Humans naturally produce cannabinoids in the nervous system to control memory, hunger, and pain.
Still too much cannabis science?
Smoke pot. Be stoned. Feel better. Science!
Stop by Torrey Holistics, San Diego’s finest legal medical marijuana dispensary, and a Cannabis Consultant will be happy to share more knowledge and tips 1 on 1.
1. Grotenhermen, Franjo (23 July 2012). “The Therapeutic Potential of Cannabis and Cannabinoids” Dtsch Arztebl Int. 109 (PMC3442177): 495–501.



